How Drone Use Optimizes Industries
In today’s rapidly evolving world, the use of drones has revolutionized various industries, offering innovative and efficient solutions to complex tasks. From capturing breath-taking aerial images to delivering packages with precision, drones have become indispensable in diverse terrains and contexts. The term “drone application method” simplifies the description of their utilization, allowing us to categorize their uses into distinct groups. Whether it’s through sensing methods like photography and surveying or action-oriented interactions like spraying and delivery, drones have proven their versatility and effectiveness. By exploring these application methods, we gain valuable insights into the remarkable capabilities of drones and their impact on different industry verticals.
Application Methods: the Use of Drones for Work
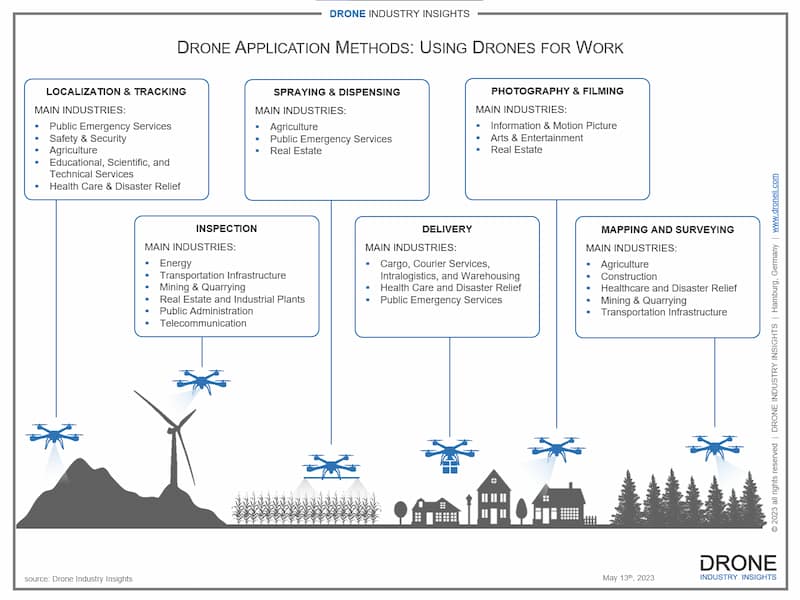
As the infographic above shows, drones can be used in all types of terrains and contexts to carry out tasks more efficiently than a human or other machines. “Drone application method” may sound like heavy jargon, but it helps avoid long formulations such as “the use of drones for photographing sites” (application method: photography) or “drone use for surveying land” (application method: surveying). And although there can be a myriad of highly-specific terms to describe what drones do (e.g. monitor, survey, spray, drop, collect, dispense, etc.), the majority of drone uses can be grouped and structured as described in the following paragraphs.
One category of drone uses is made up of sensing methods, where data is recorded by the drone without any physical contact with other objects. The most well-known of these is Photography and Filming, which involves the aerial use of cameras to capture images and for the production of aerial videos. Meanwhile, Mapping and Surveying is focused on creating a simple or very accurate representation of a given area to study or measure altitudes, angles, distances. Inspection entails the examination of a given object to find faults, errors, malfunctions or other specific phenomena that might affect the functioning of it. Finally in this group, Localization and Tracking is used to observe, seek and supply the geographical coordinates of activities, persons or life-stock, or detecting certain activities.
Another category to classify the use of drones is action/interaction methods. Most prominently in this category, we find two types. Spraying and Dispensing is defined as the aerial distribution of solids (e.g. fertilizer or seeds), or the process of spreading liquid substances (e.g. water, insecticide or fertilizer). The second and more talked about method is Delivery, which is of course the transportation of packages, food, pharmacies, or other goods either on demand or according to a given schedule.
Within these two groupings, we can nevertheless create “Other methods” such as warehousing, measuring, contact sensing, illuminating, or transmitting. These application methods would fit less neatly into the sub-categories above but are still relatively common drone uses throughout the industry. With all of this said, it is time to turn our attention from specific drone application methods to industry verticals as a whole.
Industry Verticals: Drone Use Within Industries
When we talk about drone use for Construction, there is a lot that they could actually be doing, such as for example: drones can carry out aerial imagery for site planning, management and communication (photography & filming method); they can also survey construction sites and produce topographic surveys or 3D reconstructions (mapping & surveying method); and we also often see the use of drones for monitoring construction sites to avoid illegal trespassing or thefts of site assets or supplies (localization & tracking method).
Similarly for drones in Agriculture, where they could identify/locate dead, hurt, or sick animals (inspection method in the animal production sub-vertical), or spray crops with pesticides or insecticides (dispensing & spraying method in crop production sub-vertical), or carry out forest inventory and crop health monitoring (mapping & surveying method in the forestry sub-vertical).
Our infographic shows, for example, that the Inspection method is most common in Energy, Transportation, and Mining among other industries. Alternatively looking at the various methods described, we could derive that in the Agriculture industry the use of drones is often for Spraying & Dispensing, Mapping & Surveying, and sometimes Localization & Tracking.
Interested in Commercial Drone Use? Check Out Our Latest Application Report Highlighting the Use of Drones!
Drone Application 2023
• 207-page drone use report featuring:
• 264 application examples of drone use
• 85 real-life case studies about the use of drones for work
• Market data and examples of drone use from around the globe
Application Report: Data on the Commercial Use of Drones
Drones have undeniably transformed industries, offering unparalleled efficiency and innovation. From capturing stunning aerial imagery to precise package delivery, drone use is far-reaching. Sensing methods like photography, surveying, and inspection enable data collection without physical contact, while action-oriented methods like spraying, dispensing, and delivery showcase their dynamic capabilities. Our latest Drone Application Report delves deeper into the advancements in the use of drone technology, featuring 264 application examples and 85 real-life case studies from companies around the world. In short, the integration of drones has undoubtedly reshaped industries, and there is much more to discover as highly-awaited regulations take effect and we embrace the future of this transformative technology.
Download our FREE Drone Application Methods Infographic
The “Drone Application Methods Infographic” shows drone use in various contexts, which highlights the use of drones for commercial purposes. Drone use has been adopted for hundreds of activities in dozens of industries, and our infographic shows exactly how drone technology is used in several fields.

Besides his financial oversight, Hendrik is an expert in aviation law and UAV regulation with more than 10 years of experience. Not only does he consult on all regulation questions, but Hendrik also writes the yearly drone investments report. Prior to launching DRONEII, at Lufthansa Technik he was the single point of contact to Civil Aviation Authorities (CAA) of Germany, Middle East and Asia.